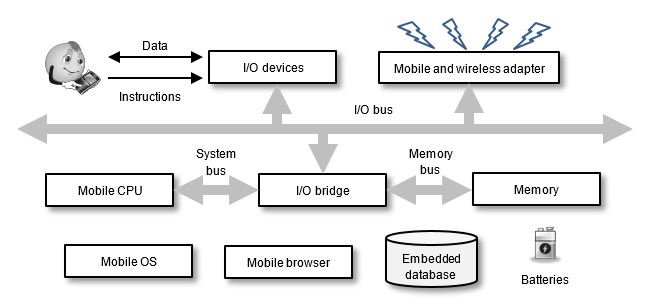
The figure shows a generic system structure of handheld devices, which includes the following six major components: (i) mobile OS, (ii) mobile CPU, (iii) mobile browser, (iv) input and output components and methods, (v) memory and storage, and (vi) batteries.
- Mobile Operating Systems (OSs)
- Simply adapting desktop operating systems for handheld devices has proved to be futile. A mobile operating system needs a completely new architecture and different features to provide adequate services for handheld devices. They are different from the traditional OSs as they include the following additional features: (i) power management, (ii) real-time capability for time-critical operations such as phone communications, and (iii) mobile and wireless infrastructure.
- Input and Output Components and Methods
- Various I/O components and methods have been adopted by mobile handheld devices. The only major output device is the screen, but there are several popular input devices, among them: (i) (soft) keyboards, (ii) touch screens/writing areas that need a stylus, and (iii) voice recognition. Special software is required for handwriting and voice recognition.
|
I always have so much fun when Katie is around — she is a barrel of laughs! (funny). |