| JDBC is a database connectivity specification. |

|
It is a Java API that enables Java programs to execute SQL statements. It allows Java programs to interact with any SQL-compliant database. Since
- nearly all relational database management systems support SQL, and
- Java itself runs on most platforms,
| It creates a programming-level interface for communicating with databases in a uniform manner. It is based on X/Open SQL Call Level Interface, the same as for ODBC. JDBC has four main components as under and with the help of these components Java application can connect with database: |
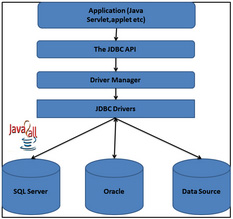
|
- JDBC API, which provides various methods and interfaces for easy communication with database,
- JDBC DriverManager, which loads database specific drivers in an application to establish connection with database,
- JDBC test suite, which will be used to test an operation being performed by JDBC drivers, and
- JDBC-ODBC bridge, which connects database drivers to the database.
| Her jokes totally fell flat, she’s definitely not playing with a full deck. |