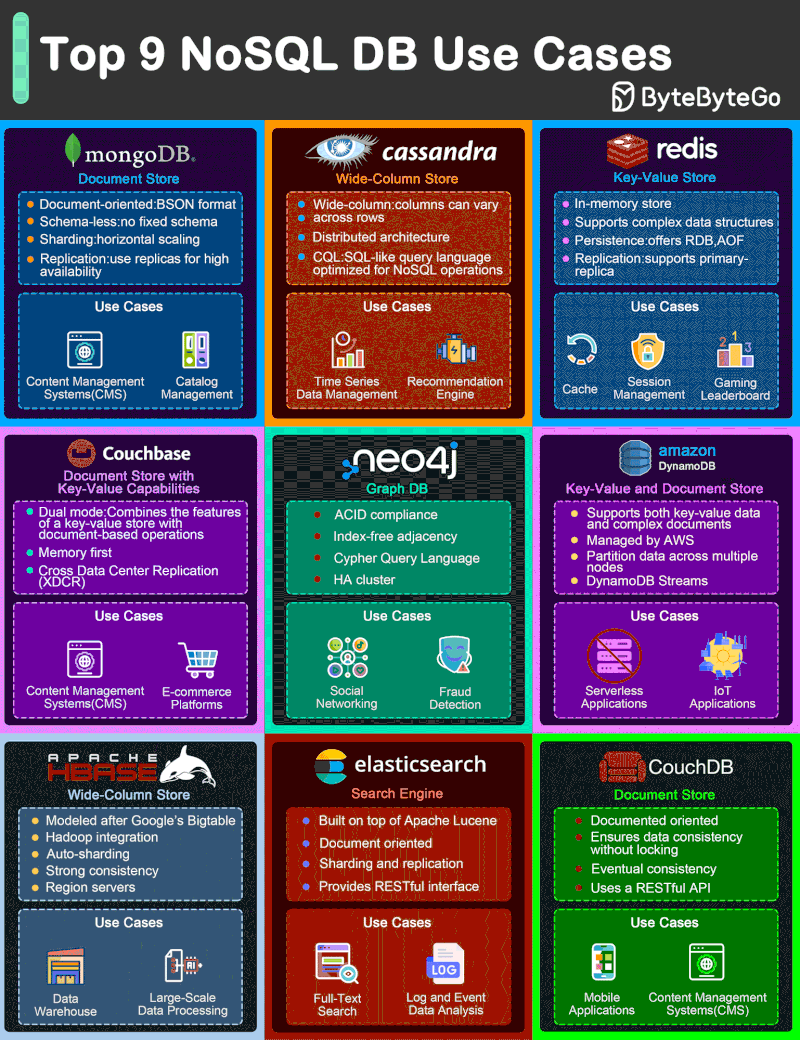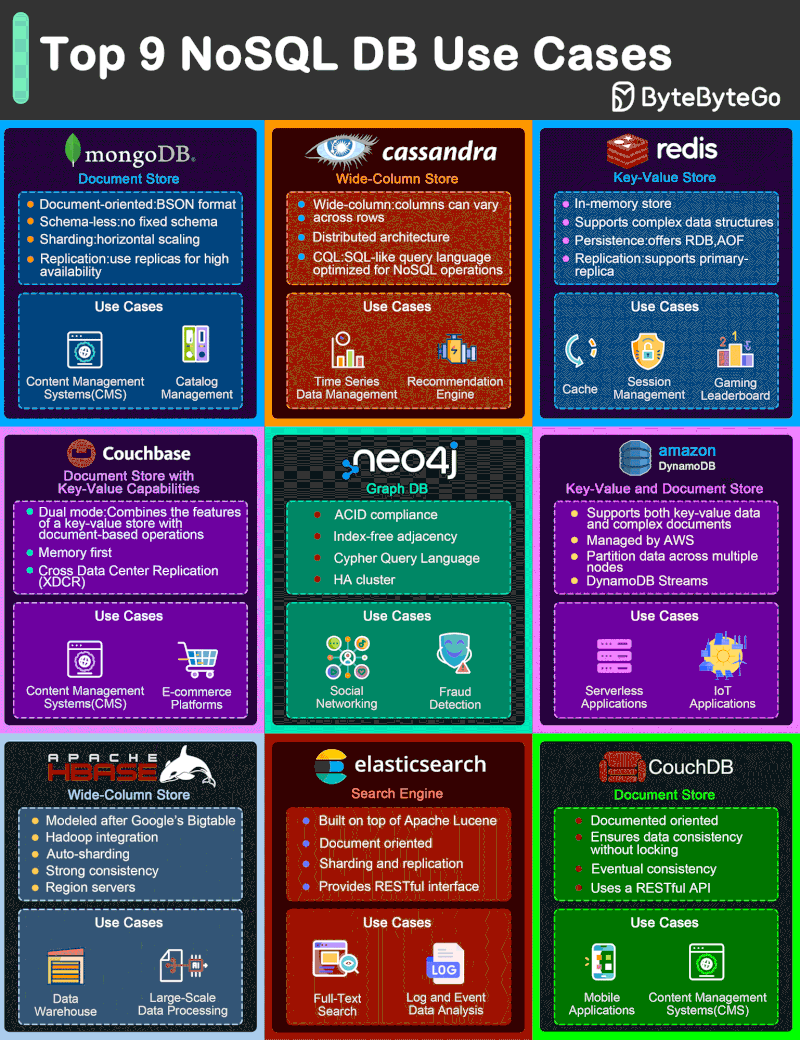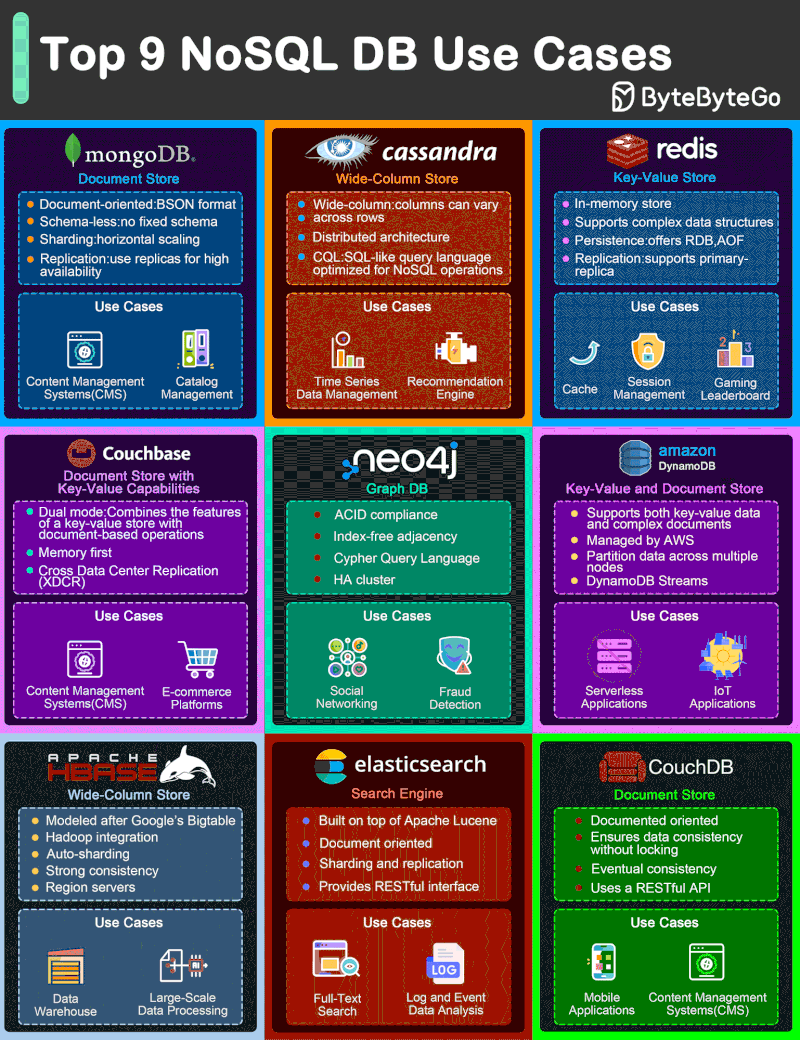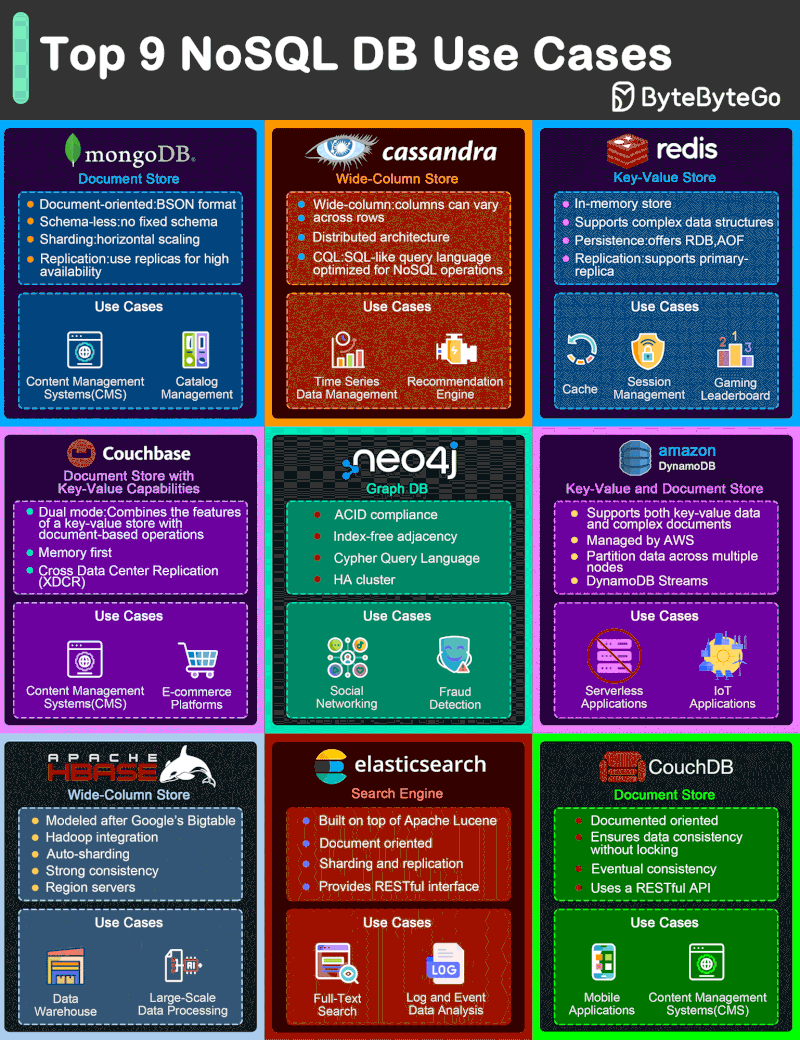
NoSQL Database Types
- Document databases (MongoDB), which pair each key with a complex data structure known as a document. Documents can contain many different key-value pairs, or key-array pairs, or even nested documents.
- Graph stores (Neo4J and HyperGraphDB), which are used to store information about networks, such as social connections.
- Key-value stores (Riak and Oracle NoSQL Database), which are the simplest NoSQL databases. Every single item in the database is stored as an attribute name (or “key”), together with its value.
- Wide-column stores (Cassandra and HBase), which are optimized for queries over large datasets, and store columns of data together, instead of rows.
| The best revenge is massive success. |