SELECT Examples
Some of SELECT examples are given next.
☠ Caution ☠: NOT all SQL commands are supported by Oracle. For a complete Oracle SQL command list, check Oracle Database SQL Language Quick Reference.
- Let
Rbe a relational schema with a set of attributesX, where {A1, ...,Ak} is contained inX. The project ofRonto {A1, ...,Ak} is expressed by
SELECT DISTINCT A1, ... Ak FROM R; SQL> SELECT DISTINCT class FROM student;
- Let
RandSbe relational schemata with equal sets of attributes. The union ofRandSis expressed by
SELECT DISTINCT * FROM R UNION SELECT DISTINCT * FROM S; SQL> SELECT DISTINCT * FROM ( SELECT last_name FROM student ) 2 UNION 3 SELECT DISTINCT * FROM ( SELECT first_name FROM student );
- Let
Rbe as in the previous slide, whereAandBare inX. The selection ofRwith respect to conditionA = ais expressed by
SELECT DISTINCT * FROM R WHERE A = a; SQL> SELECT DISTINCT last_name FROM student WHERE class = 2;
The selection with respect to conditionA = Bis expressed by
SELECT DISTINCT * FROM R WHERE A = b; SQL> SELECT DISTINCT first_name FROM student WHERE class = student_id;
Demonstration
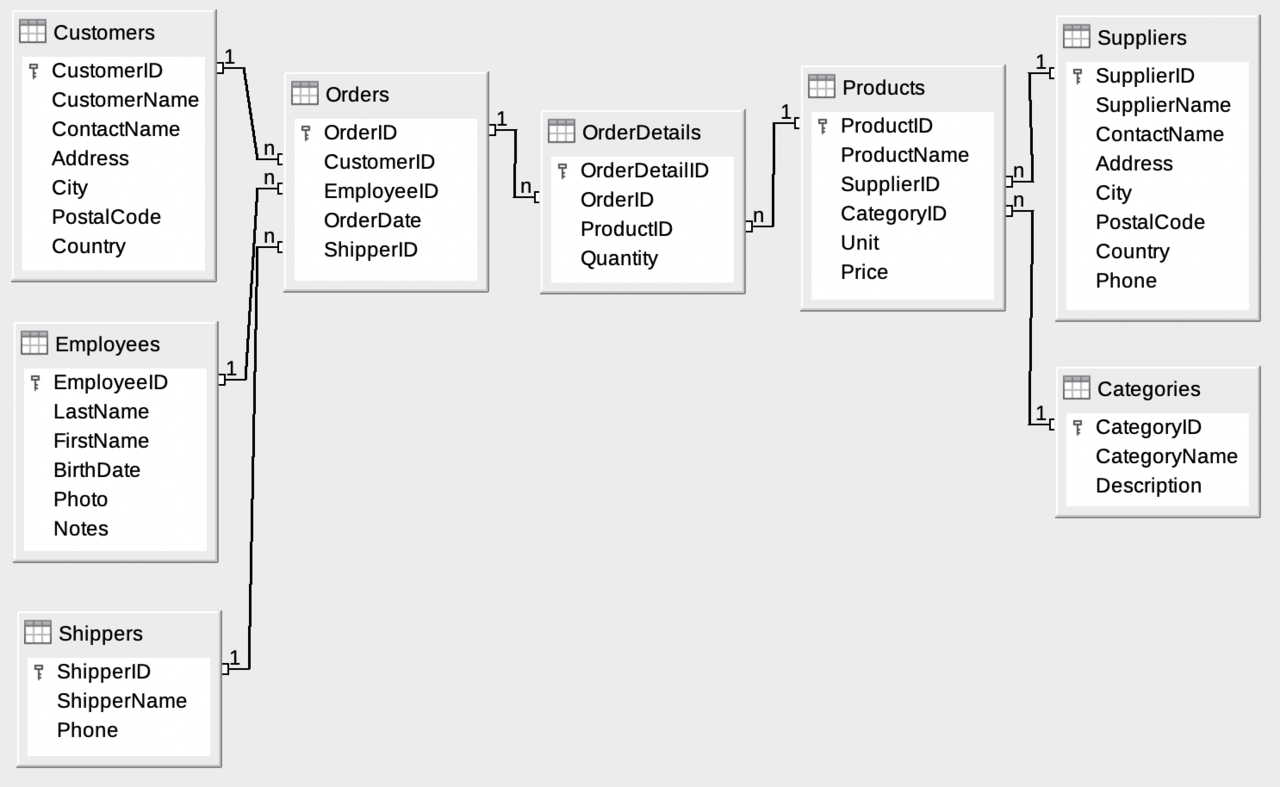
Below is an SQL test area from W3Schools, which uses the well-known Northwind sample database. The tables here are for read only because of the problem of embedding the scripts. For a fully working example, check this by using Chrome.
|
Result:
|
The Database includes:
|
|
The Database includes:
|