Transformation Rule 3. N-N Relationships
When two entities
E and F take part in an N-N relationship R:
- The many-to-many relationship
Ris mapped to a tableT. - The table
Tcontains columns for all attributes in the primary identifiers ofEandF. - The set of columns forms the primary key for
T. Talso contains columns for all attributes attached to the relationship.
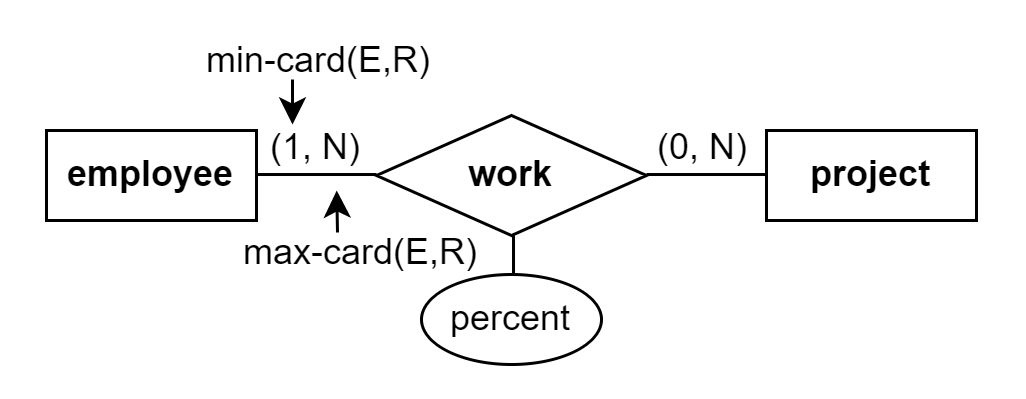
work, where an employee must work on at least one project, and a project could have no one working on it (idle).
The table work includes two columns from the primary keys of the two entities employee and project, and one column from its attribute percent.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ⇓ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
I don’t see eye to eye (agree) with Sphia on the workflow, but she’s the boss. |