The
CREATE TABLE statement is used to create a new table in a database.
The figure shows the simplified syntax of CREATE TABLE where
|
|
- The square brackets
[ ]mean the enclosed items are optional and the bar|means OR. - The column parameters specify the names of the columns of the table.
- The datatype parameter specifies the type of data the column can hold (e.g.,
VARCHAR,INTEGER,DATE, etc.). - The
NOT NULLconstraint enforces a column to NOT acceptNULLvalues, and theUNIQUEconstraint ensures that all values in a column are different. - The
AS SELECTphrase is to populate the new table by using the existing table content. - Key (
PRIMARY KEY) means an attribute or attribute combination whose values uniquely identify the tuples of any relation. - Foreign key (
FOREIGN KEY) defined for a schemaR, however, describes an attribute or attribute combination which is a key in another schemaS(REFERENCES); the meaning of a foreign key relationship betweenRandSvia attributeXis that theXpart ofRis a subset of theXpart ofS. - The
CHECKconstraint is used to limit the value range that can be placed in a column. The condition like(salary>0 AND salary<300000)must be met for the check constraint to succeed. If a constraint fails, a warning occurs and the insert or update for any offending row is skipped.
Demonstration
Below is an SQL test area from W3Schools, which uses the well-known Northwind sample database. The tables here are for read only because of the problem of embedding the scripts. For a fully working example, check this by using Chrome.
|
Result:
|
The Database includes:
|
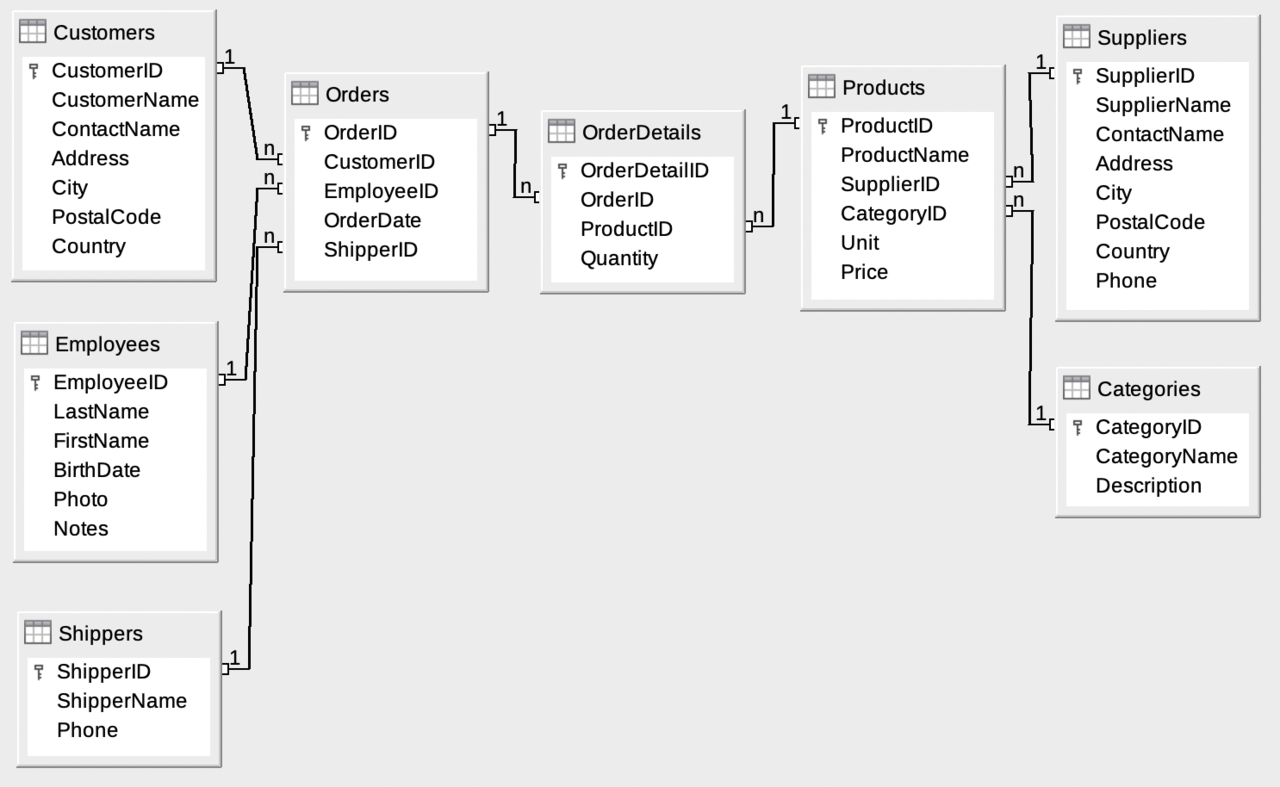
|
The Database includes:
|