| This course is related to data, which consists of three types: structured, semi-structured, & unstructured data. |

|
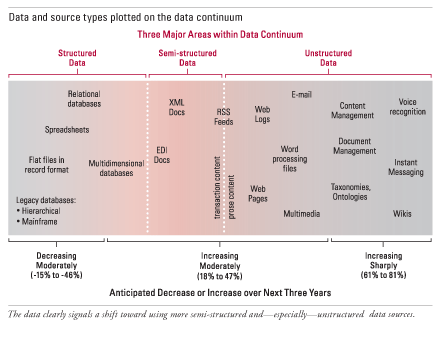
Structured Data
It is the data kept in an electronic record, where each piece of information has an assigned format and meaning; for example, the data stored in a relational database.
Semi-Structured Data
| It is a form of structured data that does not conform with the formal structure of tables and data models associated with databases but contains nonetheless tags or other markers to separate semantic elements and hierarchies of records and fields within the data; e.g., XML, HTML, and other markup languages. |
|
Unstructured Data
It is the data stored outside a formatted database; for example, presentations, e-mail messages, complicated reports, voice mail, still images, and video.
|
“We used to play spin the bottle when I was a kid,” says comedy writer Gene Perret. “A girl would spin the bottle pointed to you when it stopped, the girl could either kiss you or give you a nickel. By the time I was 14, I owned my own house.” |