|


|
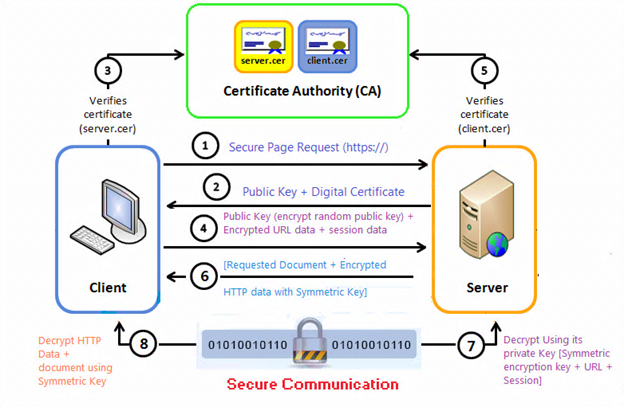
- Public key + encrypted URL data + session data, where a session key is an encryption and decryption key that is generated to ensure the security of a communications session between two computers.
- Certificate verification (client.cer), where client certificates (client.cer) are used to identify a client to a respective user, which means authenticating the client to the server.
- (Step 7 in the diagram) Decrypt using its private key (symmetric encryption key + URL + session), where the web server decrypts the symmetric encryption key using its private key and uses the symmetric key to decrypt the URL and HTTP data.
- (Step 6 in the diagram) (Requested document + encrypted HTTP data with symmetric key), where the web server sends back the requested HTML document and HTTP data encrypted with the symmetric key.
- Decrypt HTTP data + document using symmetric key, where the browser decrypts the HTTP data and HTML document using the symmetric key and displays the information.