| The following three classes are included in the only one page of this app: |
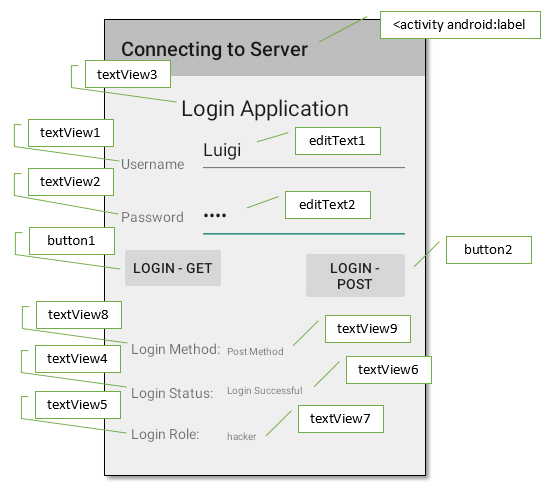
|
| Server/app/src/main/res/layout/activity_main.xml |
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android = "http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools = "http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width = "match_parent" android:layout_height = "match_parent" android:paddingBottom = "@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" android:paddingLeft = "@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingRight = "@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin" android:paddingTop = "@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context = ".MainActivity" > <EditText android:id = "@+id/editText1" android:ems = "10" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop = "40dp" android:layout_alignParentRight = "true" android:layout_alignParentTop = "true" > <requestFocus android:layout_width = "wrap_content" /> </EditText> <EditText android:id = "@+id/editText2" android:ems = "10" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_alignRight = "@+id/editText1" android:layout_below = "@+id/editText1" android:layout_marginTop = "25dp" android:inputType = "textPassword" > </EditText> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView1" android:text = "@string/Username" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_alignBottom = "@+id/editText1" android:layout_alignParentLeft = "true" /> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView2" android:text = "@string/Password" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_alignBaseline = "@+id/editText2" android:layout_alignBottom = "@+id/editText2" android:layout_alignParentLeft = "true" /> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView3" android:text = "@string/App" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop = "true" android:layout_centerHorizontal = "true" android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" /> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView4" android:text = "@string/LoginStatus" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_alignLeft = "@+id/textView8" android:layout_below = "@+id/button1" android:layout_marginTop = "80dp" /> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView5" android:text = "@string/LoginRole" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_below = "@+id/textView6" android:layout_marginTop = "27dp" android:layout_toLeftOf = "@+id/editText1" /> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView6" android:text = "@string/Status" android:textSize = "14sp" android:textStyle = "bold" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop = "3dp" android:paddingLeft = "60dp" android:layout_alignTop = "@+id/textView4" android:layout_centerHorizontal = "true" android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium" /> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView7" android:text = "@string/Role" android:textSize = "14sp" android:textStyle = "bold" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_alignBottom = "@+id/textView5" android:layout_alignLeft = "@+id/textView6" android:layout_marginLeft = "70dp" android:layout_marginBottom = "3dp" android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium" /> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView8" android:text = "@string/method" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_above = "@+id/textView6" android:layout_alignLeft = "@+id/textView5" android:layout_marginBottom = "25dp" /> <TextView android:id = "@+id/textView9" android:text = "@string/Choose" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:textSize = "14sp" android:textStyle = "bold" android:layout_marginLeft = "70dp" android:layout_marginBottom = "-3dp" android:layout_alignBottom = "@+id/textView8" android:layout_alignLeft = "@+id/textView6" android:textAppearance = "?android:attr/textAppearanceMedium" /> <Button android:id = "@+id/button1" android:text = "@string/LoginGet" android:onClick = "loginGet" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_alignBaseline = "@+id/button2" android:layout_alignBottom = "@+id/button2" android:layout_alignLeft = "@+id/textView2" /> <Button android:id = "@+id/button2" android:text = "@string/LoginPost" android:onClick = "loginPost" android:layout_width = "wrap_content" android:layout_height = "wrap_content" android:layout_centerVertical = "true" android:layout_alignLeft = "@id/textView7" /> </RelativeLayout> |