Discrete elements of information are represented in a digital system by physical quantities called signals such as voltage and currents are the most common. The signals in all present-day electronic digital systems have only two discrete values and are said to be binary. The digital-system designer is restricted to the use of binary signals because of the lower reliability of many-valued electronic circuits.
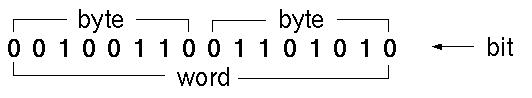
|

|
- Bits
-
Each digit in a binary number is called a bit. Typically, a 1 (on) indicates about 5 volts, and a 0 (off) indicates about 0.5 volts. Bits are numbered starting at zero on the right side, and increasing toward the left. The bit on the left is called the most significant bit (MSB), and the bit on the right is the least significant bit (LSB).


- Bytes
- Eight bits together make up a byte; it is the smallest addressable unit of storage. A byte typically holds one character.
- Words
- The size of a word in a particular computer architecture is one of its chief distinguishing characteristics. It is not absolute. It is usually the same as the width of the computer’s data bus so it is possible to read or write a word in a single operation. Modern computers usually have a word size of 16, 32, or 64 bits. A word is 32 bit (4 bytes) long on MIPS processors.
|
And God said to John, come forth and you shall be granted eternal life. But John came fifth and won a toaster. |