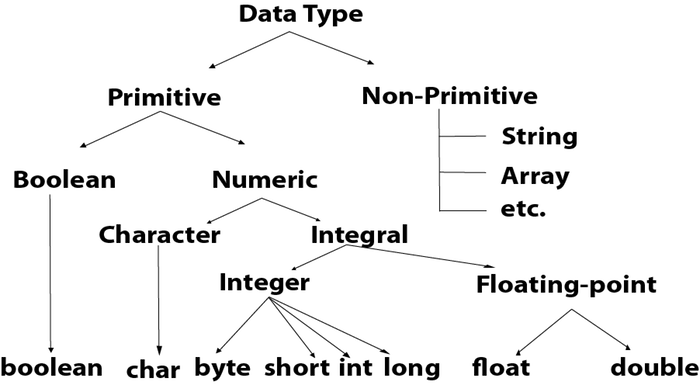
Data types specify the different sizes and values that can be stored in the variables. There are two types of data types in Java:
|
|
Primitive Data Types
A primitive data type specifies the size and type of variable values, and it has no additional methods. There are eight primitive data types in Java:
| Group | Data Type | Size | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Integer | byte |
1 byte | Stores whole numbers from -128 to 127. |
short |
2 bytes | Stores whole numbers from -32,768 to 32,767. | |
int |
4 bytes | Stores whole numbers from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. | |
long |
8 bytes | Stores whole numbers from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,808.
Note that you should end the value with an “L,” e.g., long myNum = 15000000000L; . |
|
| Floating Point | float |
4 bytes | Stores fractional numbers from 3.4e−038 to 3.4e+038. Sufficient for
storing 6 to 7 decimal digits.
Note that you should end the value with an “f,” e.g., float myNum = 5.75f; . |
double |
8 bytes | Stores fractional numbers from 1.7e−308 to 1.7e+038. Note that you should end the value with an “d,” e.g., double myNum = 19.99d; .
A floating point number can also be a scientific number with an 'e' to indicate the power of 10, e.g., float f1 = 35e3f; double d1 = 12E4d; .
|
|
| Boolean | boolean |
1 byte | Stores true or false value, e.g., boolean isJavaFun = true; .
Boolean values are mostly used for conditional testing.
|
| Character | char |
2 bytes | Stores a single character/letter.
The character must be surrounded by single quotes, like 'A' or 'c', e.g., char myGrade = 'B'; .
Alternatively, you can use ASCII values to display certain characters, e.g., char a = 65, b = 66, c = 67; .
|
|
Women only call me ugly until they find out how much money I make. Then they call me ugly and poor. |