|
|
Hierarchical and network models were developed based on graph concepts.
- Hierarchical data model
-
A kind of DBMS (DataBase Management System) that links records together like a family tree such that each record type has only one owner.
In short, the hierarchical model structured data as a directed tree, with a root at the top and leaves at the bottom.
Due to their restrictions, they often cannot be used to relate structures that exist in the real world.
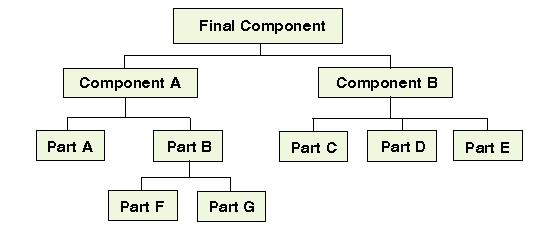


IBM’s IMS (Information Management System) was the world’s leading mainframe hierarchical data system in the 70s and early 80s. IBM replaced IMS with its relational database DB2. The main drawback for hierarchical databases is the queries against the data are difficult to create. For example, to process information about a particular part, a program would normally navigate down through the appropriate hierarchical layers.
| Living well is the best revenge. |