Trees
Tree data structure is similar to a tree we see in nature but it is upside down. It also has a root and leaves. The root is the first node of the tree and the leaves are the ones at the bottom-most level.
| The special characteristic of a tree is that there is only one path to go from any of its nodes to any other node. |
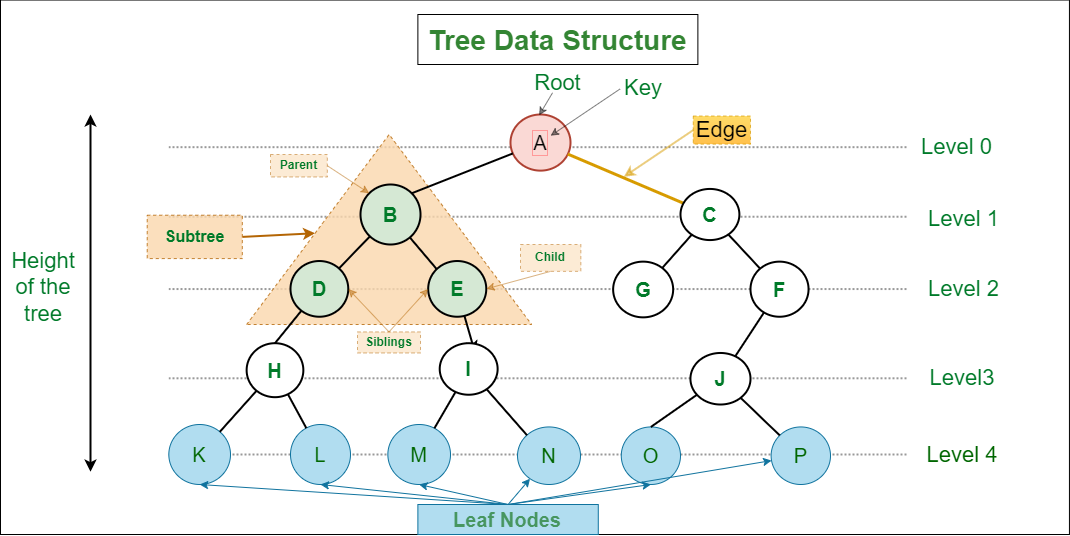
|
Graphs
It is similar to the tree data structure, with the difference that there is no particular root or leaf node, and it can be traversed in any order.
| A graph is a non-linear data structure consisting of a finite set of vertices (or nodes) and a set of edges that connect a pair of nodes. |
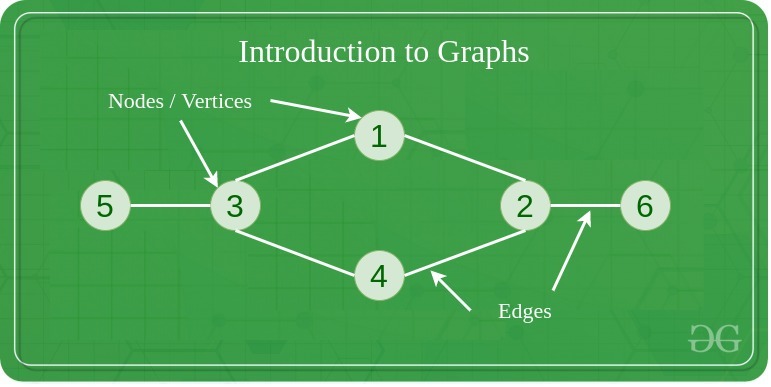
|
Heaps
A heap is a special tree-based data structure in which the tree is a complete binary tree. Generally, heaps are of two types:
- Max-heap, where the value of the root node must be the greatest among all its child nodes and the same thing must be done for its left and right sub-tree also.
|
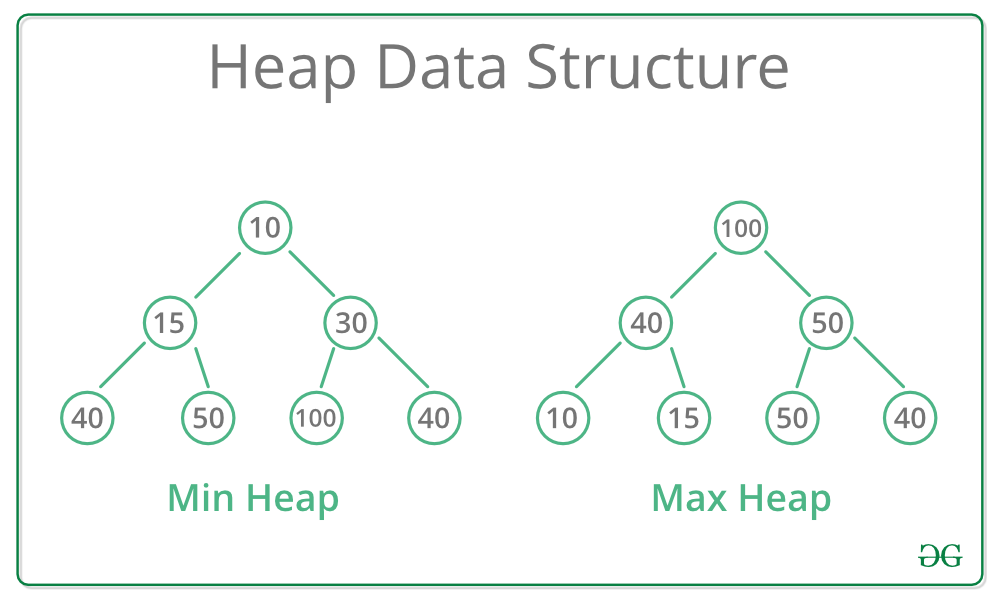
|
|
Two things are infinite — the universe and human stupidy,
and I’m not so sure about the universe. — Albert Einstein |