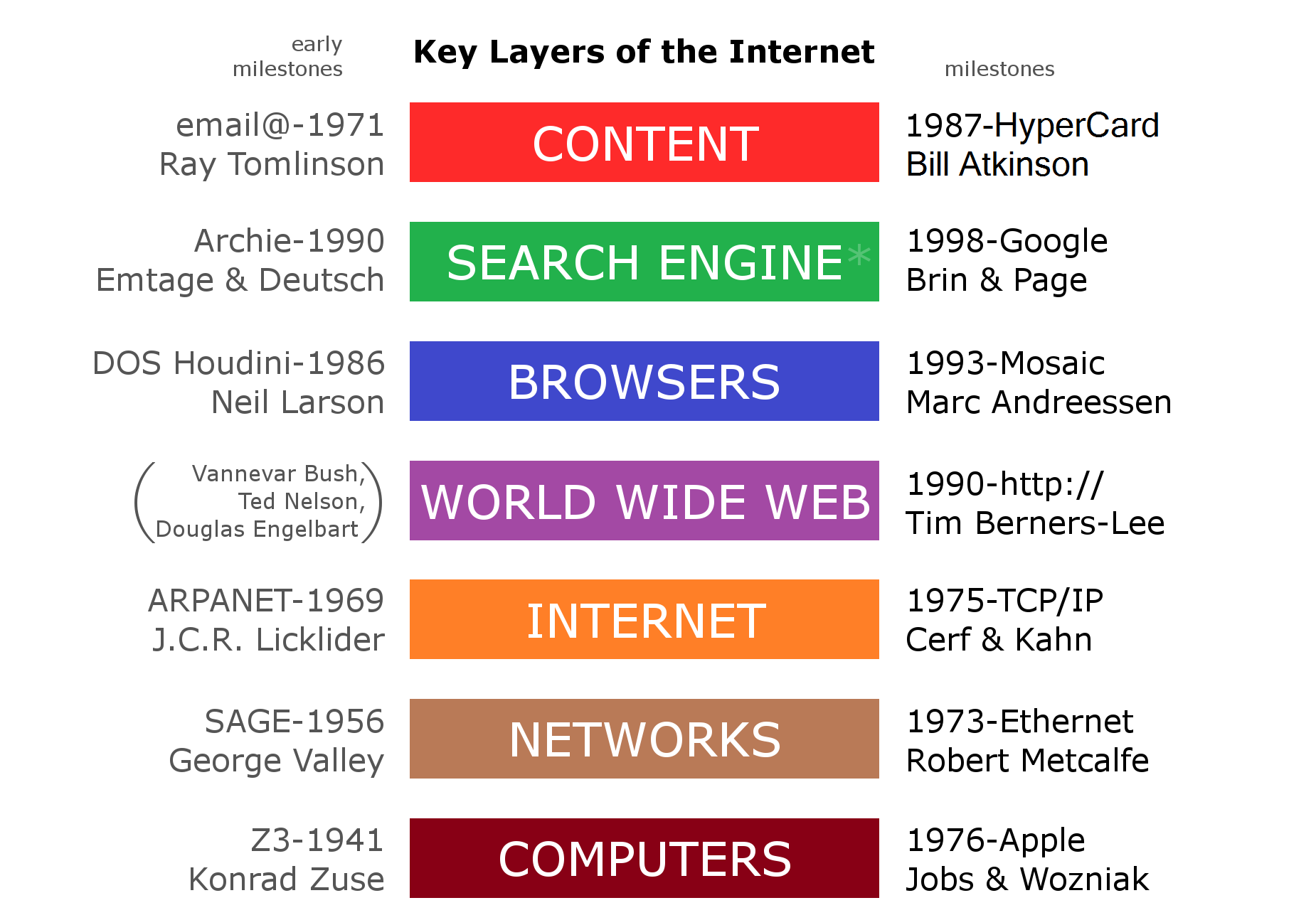
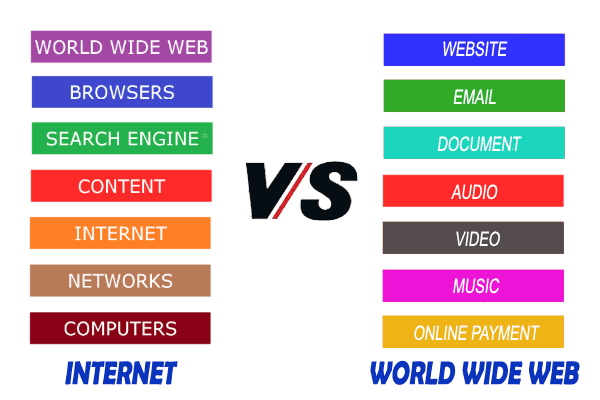
The World Wide Web (The WWW or Web)
The Web is an information system enabling documents and other web resources to be accessed over the Internet according to the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), an application layer protocol in the Internet protocol suite model for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. Documents and downloadable media are made available to the network through web servers and can be accessed by programs such as web browsers.
| Servers and resources on the Web are identified and located through character strings called uniform resource locators (URLs). The original and still very common document type is a web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). This markup language supports plain text, images, embedded video and audio contents, and scripts (short programs) that implement complex user interaction. The HTML language also supports hyperlinks (embedded URLs) which provide immediate access to other web resources. |
|
The Web runs “on top of” (figuratively) the Internet, which is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices.
|
Bob: “Looks like you’ve been missing a lot of work lately.” Peter: “I wouldn’t say I’ve been missing it, Bob.” — Bob (Paul Wilson) and Peter (Ron Lvingston), Office Space |