Week |
Class | Topic | Due | Where | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0. Computer Career and Data Research & Technologies | |||||||
| 0.1 A computer career | ||||||||
| 0.2 Data research | ||||||||
| 0.3 Data technologies | ||||||||
| 1 | 08/27 08/29 |
1. Introduction to CSCI 101 | ||||||
| 1.1 Course outline | ||||||||
| 1.2 Tentative schedule | ||||||||
| 1.3 Topics to be covered | ||||||||
| 2 | 09/03 09/05 |
2. A Computer History | ||||||
| 2.1 Historical perspective | ||||||||
| 2.2 Personal computers | ||||||||
| 2.3 Smartphones | ||||||||
| 09/03 |
Last day to add a course or drop without record — 100% refund Last day to add audit or change to/from audit Last day to receive a refund on a dropped class Drops after the last day to add will appear on a transcript. |
|||||||
| 09/01 |
|
|||||||
| 3 | 09/08 09/10 09/12 |
3. Operating Systems (OSs) | ||||||
| 3.1 OS architecture | ||||||||
| 3.2 OS process management | ||||||||
| 3.3 OS memory management | ||||||||
| 4 | 09/15 09/17 09/19 |
4. The World Wide Web (WWW) | ||||||
| 4.1 Introduction to the WWW | ||||||||
| 4.2 Internet addressing | ||||||||
| 4.3 Internet terminologies | ||||||||
| 4.3 A website architecture | ||||||||
| 5 | 09/22 09/24 09/26 |
5. Building Websites | ||||||
| 5.1 Technologies for website building | ||||||||
| 5.2 World Wide Web programming | ||||||||
| 5.3 Top tools for website development | ||||||||
| 6 | 09/29 10/01 10/03 |
6. HTML (HyperText Markup Language) | ||||||
| 6.1 Introduction to HTML | ||||||||
| 6.2 HTML tags | ||||||||
| 6.3 HTML syntax | ||||||||
| 7 | 10/06 10/10 |
7. HTML (Cont.) | ||||||
| 7.1 HTML forms and input | ||||||||
| 7.2 HTML frames and iframes | ||||||||
| 7.3 HTML5 | ||||||||
| 10/08 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 8 | 10/13 10/15 10/17 |
8. CSS (Cascading Style Sheet) | ||||||
| 8.1 Introduction to CSS | ||||||||
| 8.2 CSS basics | ||||||||
| 8.3 CSS syntax | ||||||||
| 9 | 10/20 10/22 10/24 |
9. Programming Languages | ||||||
| 9.1 Language generations | ||||||||
| 9.2 Language survey | ||||||||
| 9.3 Language processing | ||||||||
| 10 | 10/27 10/29 10/31 |
10. Data Structures and Algorithms | ||||||
| 10.1 Introduction | ||||||||
| 10.2 Data Structures | ||||||||
| 10.3 Algorithms | ||||||||
| 11 | 11/03 11/05 11/07 |
11. Databases and SQL | ||||||
| 11.1 Introduction to databases | ||||||||
| 11.2 Relational databases | ||||||||
| 11.3 SQL (Structured Query Language) | ||||||||
| 12 | 11/10 11/12 11/14 |
12. Computer Architecture | ||||||
| 12.1 Under the covers | ||||||||
| 12.2 Computer mice and monitors | ||||||||
| 12.3 Processor technologies | ||||||||
| 11/14 |
Last day to change to or from S/U grading Last day to change to or from audit grading Last day to drop a full-term course or withdraw from school |
|||||||
| 13 | 11/17 11/21 |
13. Computer Architecture (Cont.) | ||||||
| 13.1 Memory technologies | ||||||||
| 13.2 Computer networks | ||||||||
| 13.3 Chip manufacturing process | ||||||||
| 11/19 (no class) |
|
|||||||
| 14 | 11/24 | 14. Smartphones | ||||||
| 14.1 Smartphone structure | ||||||||
| 14.2 Smartphone components | ||||||||
| 14.3 Smartphone market share | ||||||||
| 11/26 11/27 11/28 |
|
|||||||
| 15 | 12/01 12/03 12/05 |
15. Smartphones (Cont.) | ||||||
| 15.1 Mobile operating systems | ||||||||
| 15.2 Mobile processors | ||||||||
| 15.3 Memory | ||||||||
| 16 | 12/08 12/10 |
16. Smartphones (Cont.) | ||||||
| 16.1 Batteries | ||||||||
| 16.2 Mobile networks | ||||||||
| 16.3 Mobile payment methods | ||||||||
| 17 | 12/15 |
|
||||||
| 18 | 12/23 | Grades posted before noon, Tuesday |
Other than some contemporary computer issues, four foundations of computer science and technologies will be covered in this course:
|
|
Instructor’s Qualification —
The instructor is well qualified for teaching this entry-level course because he has been teaching at the US universities for more than 25 years. The following list shows a range of courses being taught by him:
- CSCI 101 Introduction to Computers
- CSCI 250 Computer Organization and Programming
- CSCI 260 .NET and Web Programming
- CSCI 280 Object-Oriented Programming (Java)
- CSCI 351 Introduction to File Processing
- CSCI 370 Computer Architecture
- CSCI 399 Handheld Computing
- CSCI 457 Electronic Commerce Systems
- CSCI 513 Advanced Database Systems
- CSCI 515 Data Engineering and Management
- DATA 520 Databases
- DATA 525 Data Engineering and Mining
- CSCI 532 Programming Languages and Paradigms
- COMP 6120 Database Systems I
- COMP 6210 Compiler Construction
- COMP 7120 Database Systems II
- COMP 8140 Advanced Document Analysis and Classification Systems
An overview of the fundamental concepts and applications of computer science. Topics include data storage, hardware, operating systems, and programming principles.
The Course Missions —
This course is for non-computer-science majors, so no advanced computer knowledge and programming will be covered. After taking this course, students will be familiar with the following practical computer subjects:
- The four computer foundations: (1) programming languages, (2) computer architecture, (3) operating systems, and (4) computer algorithms and theories,
- Data storage such as databases,
- Electronic and mobile commerce systems, and
- Smartphone architecture.
| Level | Virtual Machine | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | High-level language | Examples are C, C++, and Java. |
| 4 | Assembly language | Assembly language uses short mnemonics such as ADD, SUB, and MOV that are easily translated to the machine language. |
| 3 | Operating system | The low-level software which handles the interface to peripheral hardware, schedules tasks, allocates storage, and presents a default interface to the user |
| 2 | Instruction set architecture (ISA) | Machine language. Each machine-language instruction is executed by several microinstructions. |
| 1 | Microarchitecture | A technique for implementing the instruction set of a processor as a sequence of microcode instructions |
| 0 | Digital logic | Physical machine hardware |
A Simplified Structure of an Operating System (OS) —

|

|
A System Structure of Basic Computer Systems —
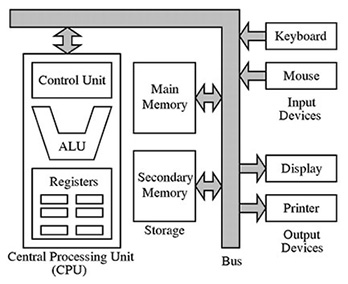
|

|
A Language Processing System —

|

|
A Mobile Handeld Device (Smartphone) —
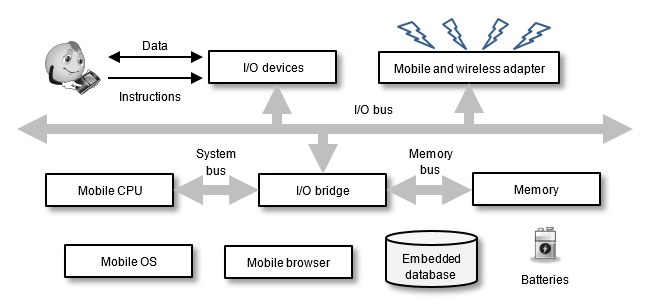
|
|