|
Computer Architecture
Computer architecture defines how a computer’s components communicate through electronic signals to perform input, processing, and output operations. |
|
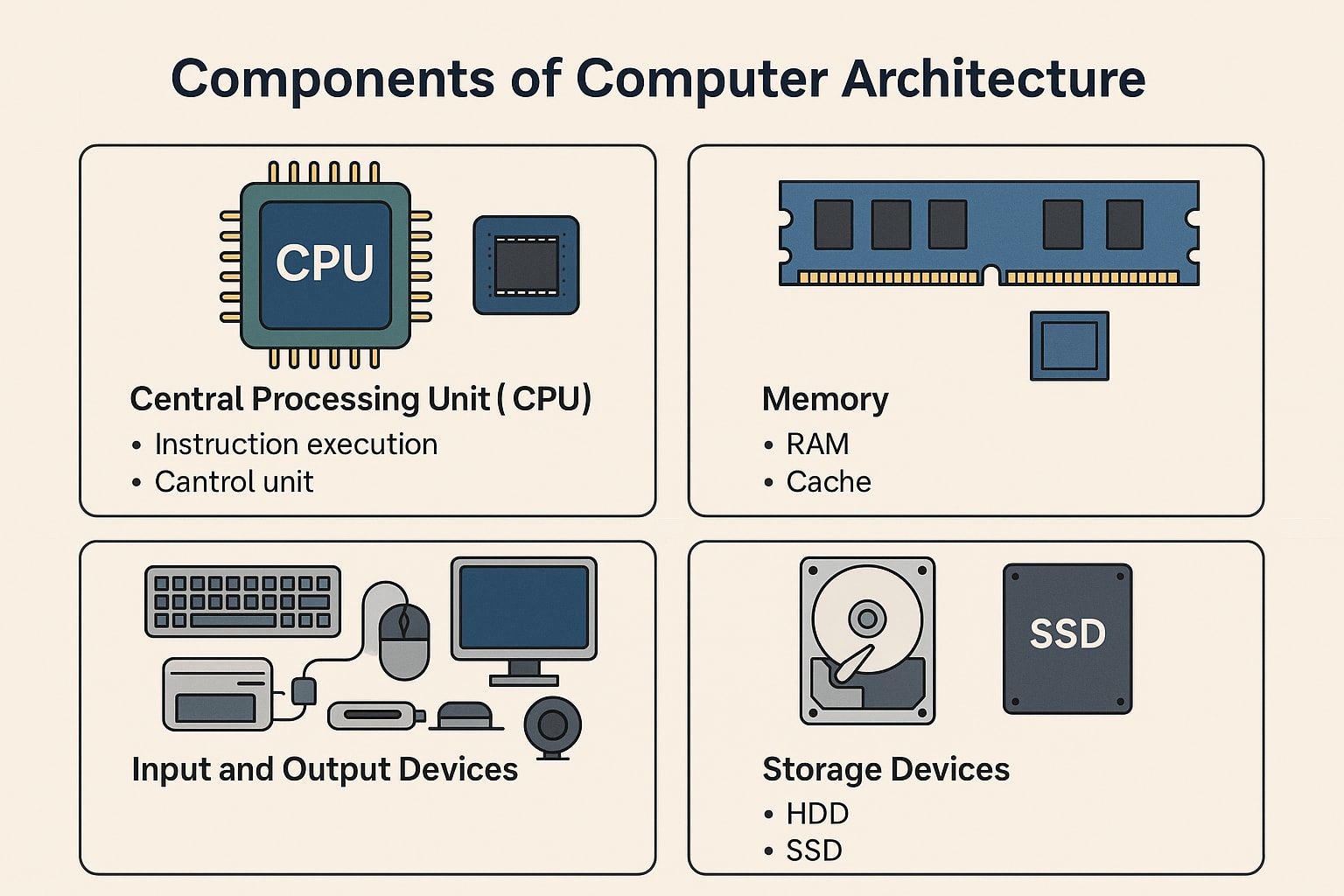
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- The CPU is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, as it is the center of all relayed operations in computer system architecture, where the CPU fetches, decodes, and executes sets of instructions at a high rate.
- Memory (RAM, Cache)
- Memory is the temporary storage unit used to hold short-term task data from users for processing by the CPU.
- Input and Output Devices
- Users and external systems communicate through an I/O device, which provides a communication link between the system and external devices. An input device includes a keyboard and a mouse. An output device includes a monitor, printer, and speakers.
- Storage Devices
-
Unlike memory, the purpose of a storage device is to provide long-term storage for all programs, files, and the operating system; e.g.,
- HDD (Hard Disk Drive): high capacity but relatively slow and
- SSD (Solid State Drive): fast, durable, and energy efficient.